Table of Contents
UI Platform Independent
Write UI source code for your screens once and start the application as a web, mobile, or desktop solution.
- Swing
Applet, Webstart or Desktop - Vaadin
HTML5/Ajax - iOS and Android
Native App for Smartphone, Tablet
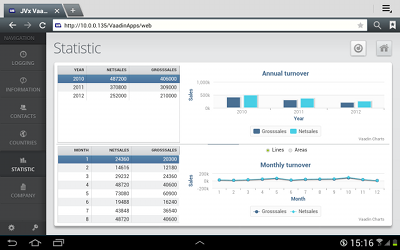
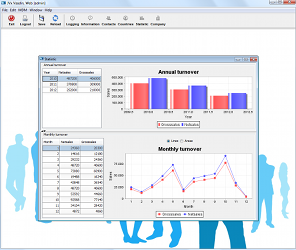

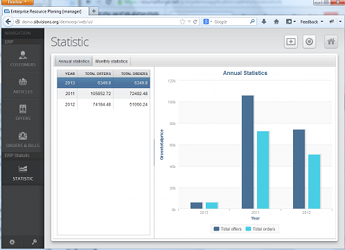
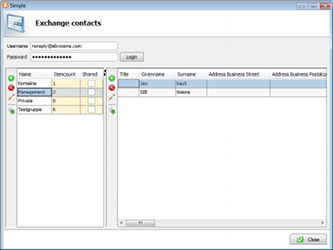
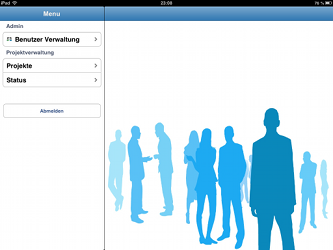
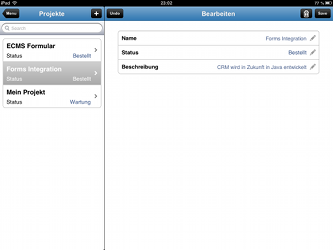
Quick and Easy Development
Client Code:
private void initializeUI() throws Exception { UITable table = new UITable(); table.setDataBook(rdbContacts);//bind to UI model add(table, UIBorderLayout.CENTER); setTitle("Contacts"); setSize(new UIDimension(600, 500)); } private void initializeModel() throws Throwable { RemoteDataBook rdbContacts = new RemoteDataBook(); rdbContacts.setDataSource(getDatasource()); // bind to DAO „contacts“ rdbContacts.setName("contacts"); rdbContacts.open(); }
Server Code:
public IStorage getContacts() throws Exception { DBStorage dbsContacts = (DBStorage)get("contacts"); if (dbsContacts == null) { dbsContacts = new DBStorage(); // Automatic DAO dbsContacts.setDBAccess(getDBAccess()); dbsContacts.setWritebackTable("CONTACTS"); dbsContacts.open(); put("contacts", dbsContacts); } return dbsContacts; }
You don't need more code!
You write just a few lines of code for an application that manages your contacts.
- initializeUI()
Initialize an UITable, bind it to the model, and add it to the screen. - initializeModel()
Instantiate model for contacts, bind it to the server, and the DAO “contacts”. - getContacts()
Instantiate DAO “contacts”, initialize it with database and table “CONTACTS”.
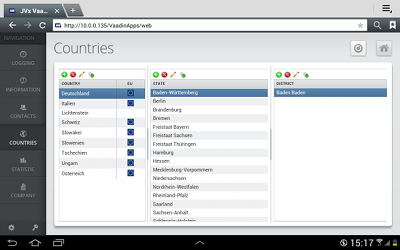
How Does It Work?
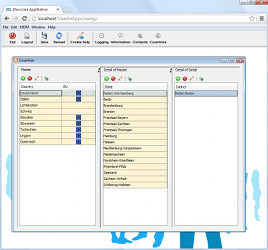
JVx' DAO class DBStorage analyzes the data model of table “CONTACTS”. This detects all data types for all columns and all foreign keys to master data tables. This metadata information is sent to the client model.
The dynamic client model, for all Daten data-bound GUI controls, uses this metadata.
Because of this mechanism, all input fields get a specific data type and size directly from the database. Dropdown lists are created because of foreign key references to master data tables, etc.
As a result, no further source code is necessary.
Covention Over Configuration
Any deviation from the standard behavior can be coded accordingly.
All Features
General
- OpenSource Framework
Apache 2.0 license - Full Stack Framework
- Full application stack, starts with GUI and ends with Persistence
- Simple APIs, short training period
- Well documented
- Easy to extend
- Database Independent
- Oracle, DB2, MS SQL, MySql/MariaDB, PostgreSql, HSQLDB, Hana, Tibero, etc.
- Applicationserver Independent
- Any servlet container, e.g., Tomcat, Wildfly, etc.
- Multi-Tier Architecture
GUI Features
- GUI Technology Independent
- Web (vaadin)
- Mobile (native iOS, Android)
- Desktop (Swing, JavaFX)
- Headless (Testing)
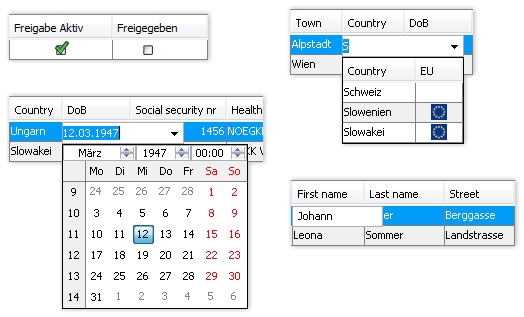
- Standardized Dynamic Model for All Data-Bound GUI Controls
- Uses persistence metadata as base datatype, data size, datatype dependent editors (e.g., “Date” → Date editor, “Master data” → Dropdown list (= Combobox)
- Editor (Number, Date, Dropdown), Table, Tree, Chart
GUI/Server Features
- Flexible Authentication Management With Different Security Managers
Database table, NTLM, LDAP, XML - CRUD Triggers on Client & Application Server
Before/After Insert, Update, Delete, Select, … - Event & Listener Concept
- Multilingual Support
- Lazy Loading
- Only visible GUI information are loaded
- No paging, lazy loading is integrated in GUI controls → scrollbar
- Process millions of records
- Flexible Application Frame
- Integrated in the framework
- Contains Toolbar, Menu, Login/out, Change password, Help, About, Save, Reload, …
- Can be easily extended and adapted to the requirements of the application
- CSS styling, Web appliaction frame
- Fully configurable application frame through interfaces
More Features
- Online Help System for Web & Desktop applications
Table of Contents, Search, HTML - User and Role Management
Database Tables, If (Rolle=Admin) Then Show Data